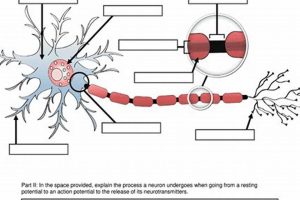
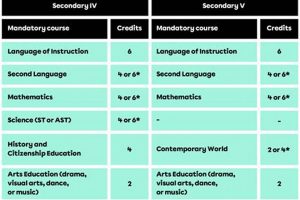
Independent, student-driven projects focused on areas of personal interest are increasingly common in secondary education. These self-directed learning experiences allow students to explore topics beyond the traditional curriculum, developing skills in research, project management, and creative problem-solving. Examples include developing a mobile application, composing a musical piece, designing a sustainable garden, or researching local history.
Such endeavors offer significant advantages for students. They foster deeper learning through active engagement and personal investment. By pursuing individual interests, students develop intrinsic motivation, enhancing their overall educational experience. Furthermore, these projects can cultivate essential skills valued by colleges and employers, such as initiative, time management, and self-directed learning. This educational approach reflects a growing emphasis on personalized learning and the recognition of diverse student talents and interests.
This article will explore various categories of projects suitable for high school students, offering practical guidance and inspiration for those seeking to embark on their own learning adventures. From scientific investigations to artistic creations and community-based initiatives, the possibilities are vast and offer a unique opportunity for students to discover their passions and build valuable skills.
Tips for Developing Successful Independent Projects
Careful planning and execution are crucial for maximizing the benefits of self-directed learning. The following tips offer guidance for students embarking on independent projects.
Tip 1: Identify a Genuine Interest: Projects rooted in genuine passion sustain motivation and lead to deeper exploration. Consider existing hobbies, curiosities, or areas of study that spark excitement.
Tip 2: Define a Clear Scope: Establish realistic goals and boundaries. A well-defined scope prevents projects from becoming overwhelming and ensures focused effort.
Tip 3: Develop a Detailed Plan: Outline the project’s phases, timelines, and required resources. A structured plan facilitates progress tracking and efficient resource allocation.
Tip 4: Seek Mentorship and Guidance: Connect with teachers, professionals, or community members with expertise in the chosen area. Mentors provide valuable insights, feedback, and support.
Tip 5: Document the Process: Maintain a detailed record of research, experiments, challenges, and solutions. Documentation showcases the learning journey and provides evidence of effort and progress.
Tip 6: Embrace Challenges and Adapt: Independent projects often involve unexpected obstacles. Developing resilience and problem-solving skills are essential components of the learning process.
Tip 7: Communicate Findings Effectively: Develop strong communication skills by presenting the project and its findings to an audience. This could involve a written report, a presentation, or a visual display.
By following these guidelines, students can transform individual interests into impactful learning experiences. These projects cultivate not only academic skills but also essential life skills such as perseverance, critical thinking, and effective communication.
These experiences offer students a unique opportunity to personalize their education and discover their potential. By embracing the challenges and rewards of self-directed learning, students prepare themselves for future success in academic and professional pursuits.
1. Exploration
Exploration forms the cornerstone of impactful independent projects, providing the driving force behind discovery and learning. It encourages students to delve into unfamiliar territories, expanding their knowledge and understanding of their chosen subjects. This process of inquiry and investigation is crucial for developing intellectual curiosity and fostering a lifelong love of learning within a high school setting.
- Curiosity-Driven Inquiry
Genuine interest fuels exploration. Students should select project topics that ignite their curiosity and inspire further investigation. For instance, a student fascinated by astronomy might choose to build a telescope or conduct research on exoplanets. This inherent curiosity propels the project forward, transforming a simple idea into a meaningful learning experience.
- Research and Information Gathering
Effective exploration involves thorough research and information gathering. Students must learn to navigate various resources, including libraries, online databases, and expert interviews. Developing research skills equips students with the tools to analyze information critically and form informed conclusions, essential skills for academic success and beyond.
- Experimentation and Discovery
Exploration often involves hands-on experimentation and discovery. Whether conducting scientific experiments, developing artistic prototypes, or building software applications, students learn through active engagement with their chosen subjects. This process encourages creative problem-solving and fosters a deeper understanding of the underlying principles at play.
- Reflection and Analysis
Exploration is not simply about gathering information; it also involves reflecting on the process and analyzing findings. Students should critically evaluate their results, identify areas for improvement, and consider the broader implications of their work. This reflective process solidifies learning and fosters critical thinking skills essential for academic and professional success.
Through exploration, students transform passive learning into active discovery. This approach fosters deeper understanding, strengthens critical thinking skills, and cultivates a lifelong love of learning. By embracing the spirit of inquiry, students embark on a journey of intellectual growth, laying the foundation for future success in their chosen fields.
2. Skill Development
Independent projects offer significant opportunities for skill development beyond traditional classroom learning. These projects allow students to acquire practical skills applicable to various academic disciplines and future career paths. The self-directed nature of these endeavors fosters crucial skills such as time management, problem-solving, and critical thinking. For example, a student developing a mobile application learns coding, project management, and user interface design, while a student researching local history develops research, analytical, and historical thinking skills.
The process of designing, planning, and executing a project necessitates effective time management. Students learn to prioritize tasks, allocate resources, and meet deadlines, essential skills for academic and professional success. Furthermore, encountering challenges and setbacks during project execution cultivates problem-solving abilities. Students must identify obstacles, analyze potential solutions, and adapt their strategies to overcome challenges, developing resilience and resourcefulness. Simultaneously, independent projects enhance critical thinking by requiring students to analyze information, evaluate evidence, and synthesize findings into coherent conclusions.
In essence, these projects serve as a bridge between theoretical knowledge and practical application. They provide students with the opportunity to apply classroom learning to real-world scenarios, deepening their understanding and enhancing their skill set. By engaging in these self-directed learning experiences, students develop valuable skills that contribute to academic achievement, career readiness, and lifelong learning. This practical application of knowledge not only reinforces learning but also fosters a deeper appreciation for the interconnectedness of various fields of study.
3. Personal Growth
Independent projects in high school offer substantial opportunities for personal growth, extending beyond academic skill development. These experiences cultivate self-awareness, resilience, and a deeper understanding of personal strengths and interests. By engaging in self-directed learning, students navigate challenges, discover hidden talents, and develop a stronger sense of self-efficacy, contributing significantly to their overall development.
- Self-Discovery and Exploration of Interests
Passion projects provide a unique avenue for self-discovery. Students explore areas of genuine interest, often beyond the confines of the standard curriculum. This exploration can lead to the identification of previously unknown talents and passions, shaping future academic and career paths. A student initially interested in coding might discover a passion for graphic design while creating a video game, leading to a more nuanced understanding of their capabilities and aspirations.
- Development of Resilience and Perseverance
Independent projects invariably present challenges and obstacles. Navigating these challenges cultivates resilience and perseverance. Students learn to adapt to setbacks, problem-solve creatively, and maintain focus despite difficulties. The experience of overcoming these obstacles builds confidence and reinforces the value of sustained effort in achieving long-term goals. For example, a student building a robot for a competition learns to troubleshoot technical issues, fostering persistence and problem-solving skills.
- Enhanced Self-Confidence and Self-Efficacy
Successfully completing a challenging project fosters a sense of accomplishment and boosts self-confidence. Students witness the tangible results of their efforts, strengthening their belief in their ability to achieve goals. This increased self-efficacy motivates them to undertake future challenges with greater confidence and a stronger sense of self-reliance. Presenting research findings at a local conference, for instance, can significantly boost a student’s self-assurance and belief in their research capabilities.
- Cultivation of Self-Management and Organizational Skills
Managing a project independently requires strong self-management and organizational skills. Students learn to plan, prioritize, and execute tasks effectively, developing valuable time management and organizational habits. These skills extend beyond the project itself, benefiting academic performance and other areas of life. A student organizing a community event, for example, develops logistical planning and coordination skills, valuable assets in various future endeavors.
These aspects of personal growth cultivated through independent projects contribute significantly to a student’s holistic development. The skills and self-awareness gained extend beyond the immediate project, shaping their approach to learning, problem-solving, and personal fulfillment. These experiences empower students to take ownership of their learning and development, preparing them not only for academic success but also for the challenges and opportunities of adult life.
4. Academic Enhancement
Independent project work significantly enhances academic performance in high school by providing opportunities for in-depth exploration, practical application of knowledge, and development of essential skills. These projects bridge the gap between theoretical concepts learned in the classroom and real-world application, leading to a deeper understanding and retention of information. They also foster critical thinking, research skills, and problem-solving abilities, all crucial for academic success.
- Deeper Understanding of Subject Matter
Passion projects allow students to delve deeper into subjects of interest, moving beyond the surface level curriculum. This focused exploration fosters a richer understanding and encourages connections between different concepts. A student passionate about history, for example, might research a specific historical event in detail, gaining a more nuanced understanding of its causes, consequences, and significance than a traditional textbook approach would allow.
- Practical Application of Knowledge and Skills
These projects offer students the opportunity to apply theoretical knowledge to practical situations. This hands-on experience solidifies learning and demonstrates the real-world relevance of academic concepts. A student studying physics, for instance, could design and build a working model demonstrating a specific physical principle, reinforcing their understanding of the concept and developing practical engineering skills.
- Development of Critical Thinking and Research Skills
Independent projects necessitate critical thinking and research skills. Students must formulate research questions, evaluate sources, analyze data, and draw informed conclusions. These skills are transferable across disciplines and essential for success in higher education. A student researching the environmental impact of plastic pollution, for example, develops critical thinking skills by evaluating different perspectives and research methodologies.
- Enhanced Communication and Presentation Skills
Many projects culminate in a presentation or report, providing opportunities to develop communication and presentation skills. Students learn to articulate their ideas clearly and concisely, both orally and in writing. This experience builds confidence and prepares them for future academic and professional presentations. A student presenting their research on renewable energy sources, for instance, hones their public speaking and data visualization skills.
By fostering deeper understanding, practical application, and critical thinking, independent projects contribute significantly to academic growth. They empower students to take ownership of their learning and develop essential skills that extend beyond the classroom, preparing them for success in higher education and beyond. The combination of personal interest and academic rigor creates a powerful learning experience, fostering a lifelong love of learning and a deeper appreciation for the interconnectedness of knowledge.
5. Real-world application
Connecting high school projects to real-world applications significantly enhances their educational value. This connection transforms theoretical knowledge into practical experience, demonstrating the relevance of academic concepts in addressing real-world challenges. Such application fosters deeper understanding, strengthens critical thinking skills, and cultivates a sense of purpose and impact. Consider a student designing a prosthetic limb using 3D printing technology. This project combines engineering principles with problem-solving to address a real-world need, offering a tangible demonstration of the project’s impact.
Practical applications can manifest in various forms. Developing a mobile application to assist local businesses connects technology with entrepreneurship and community engagement. Creating a documentary film about local environmental issues combines storytelling with advocacy, raising awareness about real-world problems. Designing and implementing a recycling program within a school demonstrates environmental responsibility and community leadership. These examples illustrate how project-based learning bridges the gap between classroom learning and real-world problem-solving, fostering valuable skills and a sense of civic engagement. This approach not only deepens understanding but also empowers students to become active and informed contributors to their communities.
Understanding the practical significance of real-world application is crucial for maximizing the educational benefits of project-based learning. It fosters a sense of purpose, demonstrating the tangible impact of academic pursuits. While challenges such as resource constraints or access to mentorship may arise, the potential benefits outweigh the difficulties. Integrating real-world applications into project design fosters innovation, creativity, and a deeper connection between learning and societal contribution. Ultimately, this approach prepares students to become engaged citizens equipped to address complex challenges and contribute meaningfully to the world around them.
6. Community Engagement
Community engagement offers a valuable dimension to high school passion projects, connecting student learning with real-world issues and local needs. Integrating community engagement into project design fosters civic responsibility, strengthens practical skills, and provides opportunities for students to contribute meaningfully to their surroundings. This connection enriches the learning experience while simultaneously benefiting the community.
- Addressing Local Needs
Projects can address specific community needs, offering tangible solutions to local challenges. Examples include developing a public awareness campaign about local environmental issues, organizing a fundraising event for a local charity, or creating a community garden to address food insecurity. These projects empower students to become active agents of change within their communities, fostering a sense of civic responsibility and demonstrating the practical application of their skills and knowledge.
- Collaboration with Community Organizations
Partnering with local organizations provides students with real-world experience and mentorship opportunities. Collaborations with environmental groups, historical societies, or social service agencies offer valuable insights into community dynamics and professional practices. Working alongside experienced professionals exposes students to diverse perspectives and strengthens their understanding of community issues. This collaborative approach enhances the project’s impact and provides students with valuable networking opportunities.
- Developing Civic Responsibility
Engaging with the community fosters civic responsibility and encourages students to become active and informed citizens. By addressing local challenges and contributing to community well-being, students develop a deeper understanding of their roles and responsibilities within society. This experience instills a sense of ownership and empowers them to become active participants in shaping their communities’ future. Projects like organizing voter registration drives or participating in local government meetings cultivate civic engagement and prepare students for responsible citizenship.
- Gaining Real-World Experience
Community-engaged projects provide invaluable real-world experience, complementing classroom learning. Students develop practical skills in project management, communication, teamwork, and problem-solving. These experiences enhance their resumes and college applications, demonstrating their commitment to community involvement and their ability to apply their knowledge in practical settings. The skills and experiences gained through community engagement prepare students for future academic and professional pursuits.
By incorporating community engagement into passion projects, high school students gain a deeper understanding of their local context, develop valuable skills, and contribute meaningfully to society. These experiences not only enhance their academic learning but also foster civic responsibility and prepare them for engaged citizenship. The connection between project-based learning and community engagement creates a powerful synergy, enriching both the student’s educational journey and the community’s well-being.
Frequently Asked Questions
This section addresses common inquiries regarding student-driven projects, providing clarity and guidance for those seeking to embark on these enriching learning experiences.
Question 1: How much time should be dedicated to an independent project?
Time commitment varies depending on project scope and complexity. Establishing a realistic timeline during the planning phase ensures manageable progress. Regular, dedicated work periods, even if short, contribute significantly to long-term progress.
Question 2: What resources are available to support project development?
Numerous resources exist, including school libraries, online databases, community organizations, and mentors. Educators can provide guidance on accessing relevant resources and connecting with potential mentors. Resourcefulness and proactive exploration are key to maximizing available support.
Question 3: How can project feasibility be assessed before commencement?
Careful consideration of available resources, required skills, and potential challenges helps determine feasibility. Discussing project plans with educators or mentors provides valuable feedback and ensures realistic expectations. Thorough planning and risk assessment are essential for successful project completion.
Question 4: What if the chosen project proves too challenging or unmanageable?
Adaptability is crucial. Reassessing project scope, seeking guidance, or adjusting objectives allows for continued progress despite challenges. Viewing challenges as learning opportunities fosters resilience and problem-solving skills.
Question 5: How can project outcomes be effectively communicated or showcased?
Various methods exist, including written reports, presentations, visual displays, or digital portfolios. Choosing a method aligned with project goals and target audience ensures effective communication of findings and impact.
Question 6: How can these projects benefit future academic or career pursuits?
Demonstrating initiative, time management, and problem-solving skills through project work strengthens college applications and resumes. These experiences provide tangible examples of self-directed learning and a commitment to pursuing individual passions, valuable assets for future academic and professional endeavors.
Engaging in self-directed learning experiences requires careful planning, resourcefulness, and a willingness to embrace challenges. The potential rewards, however, extend far beyond the immediate project, contributing significantly to academic growth, personal development, and future success.
Further resources and guidance on developing impactful projects can be found [link to relevant resources or next section].
Conclusion
Exploration of appropriate project concepts for secondary students reveals significant potential for academic enrichment, skill development, and personal growth. Careful consideration of individual interests, coupled with thorough planning and effective resource utilization, maximizes project impact. From community-engaged initiatives to technically focused endeavors, opportunities abound for students to cultivate valuable skills and contribute meaningfully to their surroundings. Focusing on real-world applications strengthens the relevance of academic pursuits and prepares students for future challenges.
Independent project pursuits offer a unique avenue for students to discover passions, develop essential skills, and contribute positively to society. Embracing these opportunities empowers students to shape their educational journeys and prepare for future success in a rapidly evolving world. The integration of such projects into educational frameworks underscores a commitment to fostering well-rounded individuals equipped to navigate complex challenges and contribute meaningfully to the global community.